WordPress Security
What are some of the security vulnerabilities with WordPress websites? Define briefly in your own words.
Some security vulnerabilities for a WordPress Website Are:
- Old versions of themes or plugins. – A theme or plug in should always be kept up to date to help prevent attacks on your website.
- Unauthorized Access – Access gained by using a poor password, a Brute Force Attack
- Not having a security plugin. – Some security plugins can scan your site to help detect malware. They could also help create backups of your website that you could use to restore your site if you were attacked.
How do you harden WordPress website? Mention at least 15-20 different settings or techniques or tricks.
- Keep your plugins and themes up to date
- Use Strong Passwords
- Use a Multi Factor Authentication
- Limit the Number of Logi Attempts
- Require Users on your Website to use Strong Passwords
- Regularly Backup Your Website
- Install an SSL Certificate
- Install a Security Plugin
- Delete Unnecessary or Outdated Plugins
- Have Inactive Users Automatically Logged Out
- Have an Alert Set for Suspicious Logins
- Secure Your WP-Config File
- Only Allow Users Access to Files Who Need Access
- Only Install Trusted Plugins to Your WordPress Site
- Hide the Version of WordPress That You Use
What plugins/resources are available for WordPress Security? Name at least five plugins or resources and what services or benefits do they provide.
Some plugins/resources that are available for WordPress Security are:
- Jetpack – Services provided by the plugin:
- Malware Scanning
- Protection Against Brute Force Attacks
- Two-Factor identification
- Detects Vulnerabilities in a WordPress Website
- Keeps an Activity Log
- Wordfence – Services provided by the plugin:
- Malware Scanning
- Firewall Protection
- Brute Force Protection
- Login Protection
- Two-Factor identification
- Wordfence has a free version
- Sucuri – Services provided by the plugin:
- Firewall Protection
- Bot Protection
- Scans the Server-Side
- Protection from Brute Force Attacks
- Detects Vulnerabilities
- Keeps an Activity Log
- Offers Malware Cleanups
- Security Ninja – Services provided by the plugin:
- Creates Backups of a Website
- Firewall Protection
- Malware Scanning
- Creates an Event Log
- Detects Vulnerabilities
- Defender
- Scans For Malware
- Two-Factor Authentication
- Bot Protection
Which plugin(s) do you think you will use and why?
I think I will use Wordfence. Its free version is rated as one of the best free versions for a WordPress Security Plugin. Also, it was recommended in the lecture for the Security Module.
What would you do if you are hacked? (Call the experts is not an answer.)
If my website were attacked, I could use a backup to restore it to a previous version before the attack. If I am being hosted my service, such as webhostingforstudent.com, I could submit a ticket asking for help to recover from getting hacked.
What is SSL? How would you activate it in your domain? Submit a screenshot of your activation. Some of you activated this past fall semester, make sure to renew your certificate if needed. Please go through the slides in Module 9 at:
https://webhostingforstudents.com/learn/curriculum/module-9-security/
My SSL Certificate:
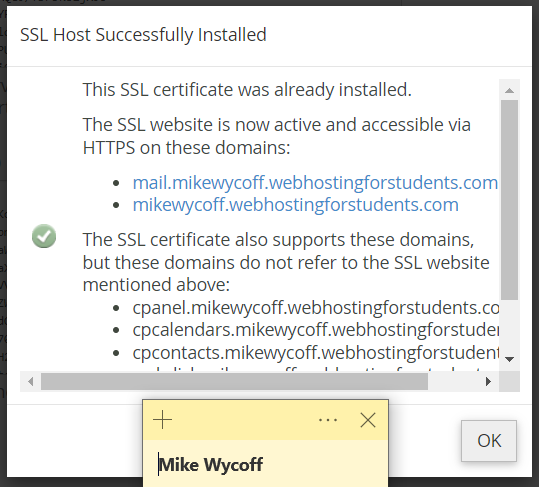
Three plugins/resources that I consider the best in my test site for this course.

Wordfence Security
Jetpack




